Unpaired Medical Image Translation
Medical image translation with adversarial diffusion models for pseudo labeling
Presented at the MICCAI 2024 workshop on deep generative models, our paper Unpaired Modality Translation for Pseudo Labeling of Histology Images was developed during a research internship with Julien Cohen-Adad at the NeuroPoly Lab from October 2023 to April 2024. This paper addresses the critical challenge of data scarcity in medical segmentation tasks, which is especially acute in histology imaging where researchers often have annotated data in one modality but lack it in another that is of interest. Our approach introduces a novel way to generate annotations in the target modality using existing labeled data, thus bridging this gap.
Methods
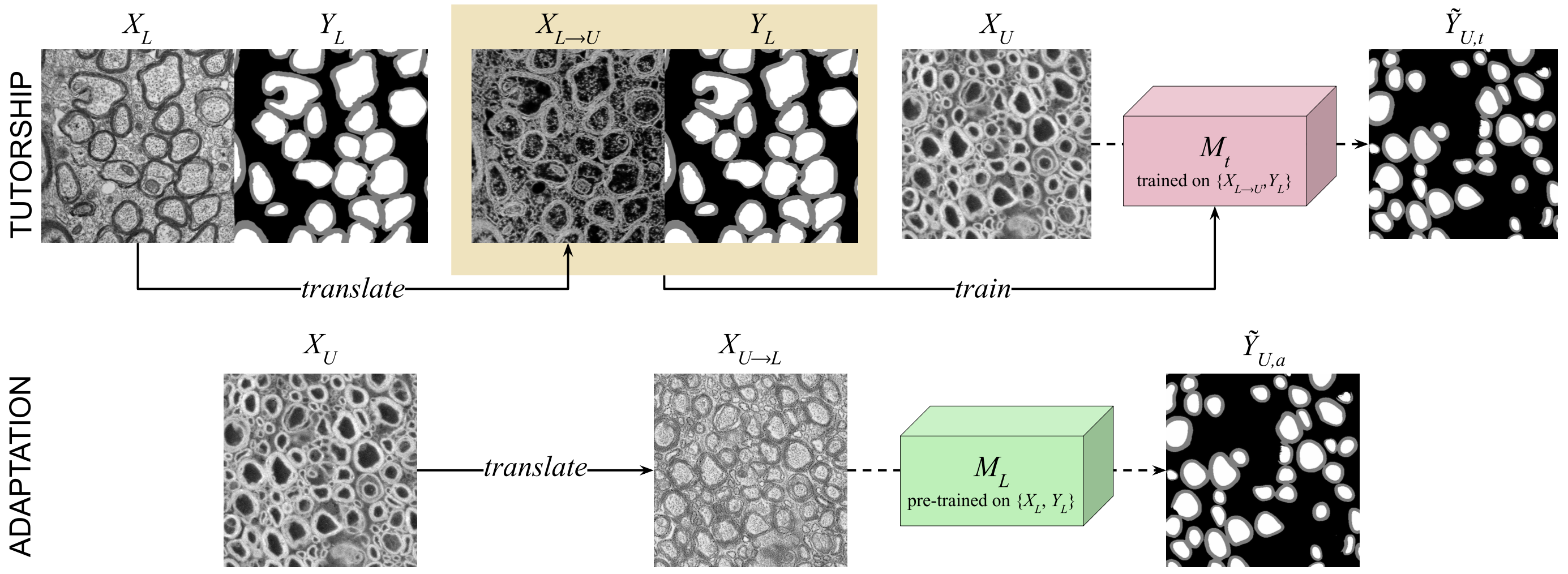
Our methodology leverages the adversarial diffusion model, SynDiff, for unsupervised image translation, enabling the generation of pseudo labels without prior annotations in the target domain. We propose two pseudo labeling strategies to facilitate this translation:
- Tutorship: This strategy involves training a proxy segmentation model on synthetic data derived from translating labeled images from one modality (e.g. TEM) to an unlabeled target modality (e.g. SEM).
- Adaptation: This strategy converts unlabeled images to match the labeled data distribution, thereby enabling segmentation with a pre-trained model.
These strategies were rigorously tested across three distinct image domains that varied significantly in similarity to the labeled data, evaluating their adaptability and effectiveness under various conditions.
Results
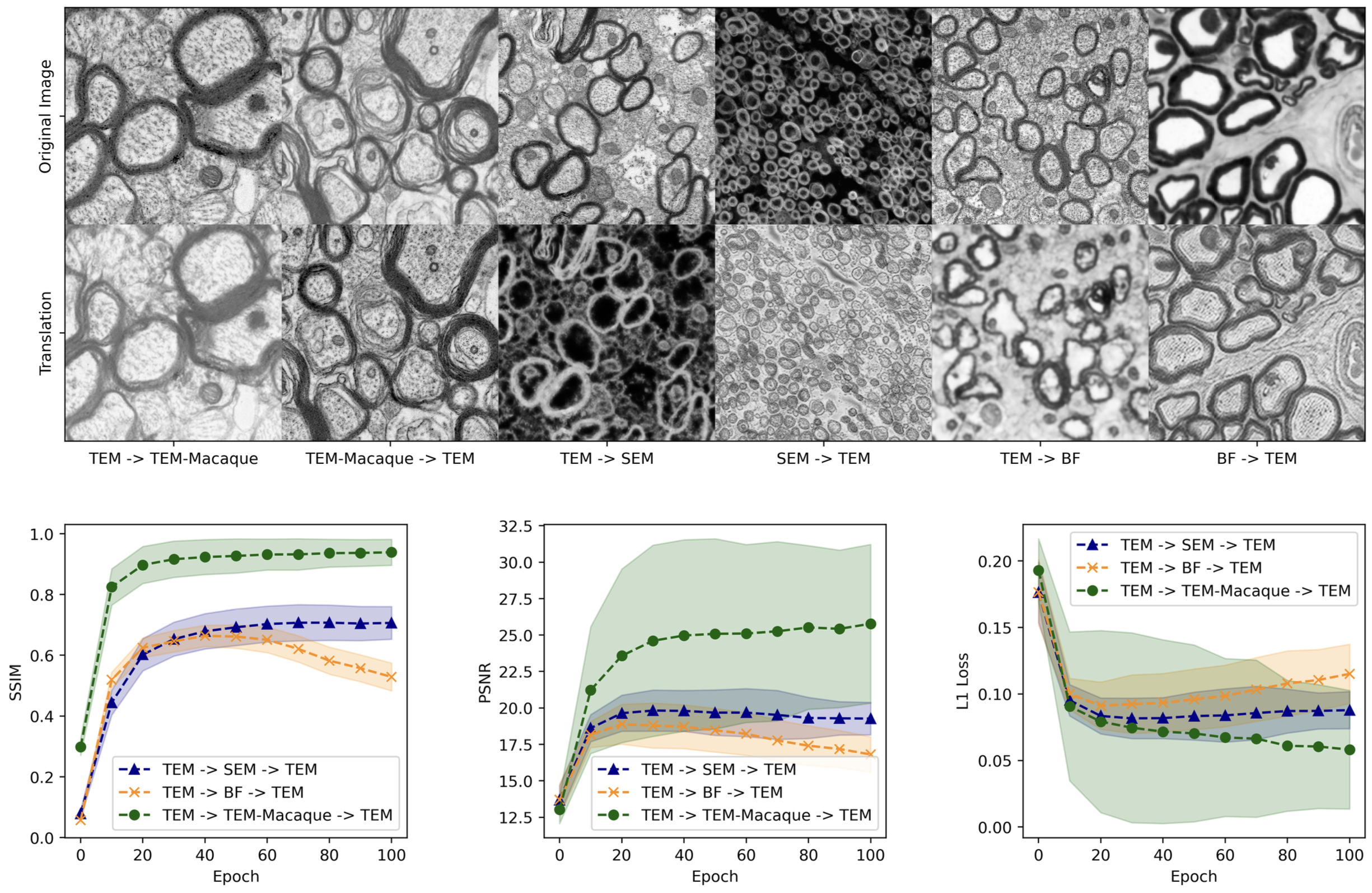
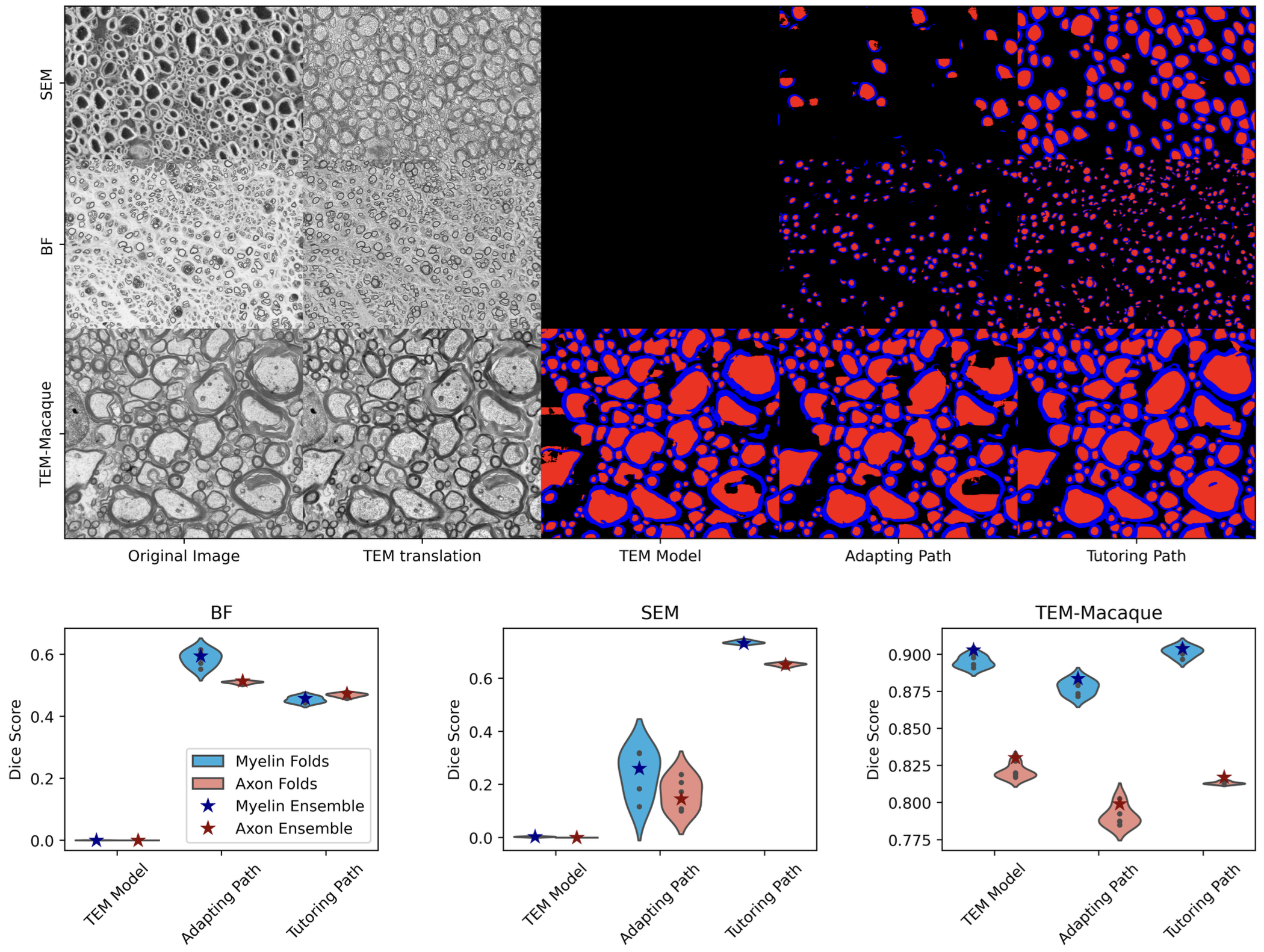
Our findings, as detailed in the paper, underscore the potential of our methods to significantly alleviate the issue of data scarcity in medical image segmentation:
- SEM Dataset: The tutorship strategy achieved a mean Dice score of 0.736, demonstrating its efficacy in generating useful pseudo labels for SEM images, which are typically difficult to annotate due to their unique properties.
- Performance Across Domains: While the adaptation strategy is more suited to settings with minimal domain shifts, the tutorship approach excels in more challenging environments, making it a robust solution for significant modality differences.
This project not only provides a viable solution to the lack of annotated medical imaging data in different modalities but also paves the way for more effective and efficient medical research and diagnostics by leveraging existing annotations more broadly.
For more details, check out the paper and the code in our repository .